Prepare for an epic journey through time with the World History Semester 1 Exam. This exam is your passport to unlocking the secrets of the past, from ancient civilizations to modern marvels. Embark on a quest for knowledge and discover the captivating stories that shaped our world.
Delve into the depths of historical periods, explore diverse geographical regions, and meet the iconic figures who left an indelible mark on humanity. This exam is not just a test; it’s an adventure that will ignite your curiosity and expand your understanding of the world.
Introduction
The World History Semester 1 Exam is a comprehensive assessment designed to evaluate students’ understanding of the key concepts, events, and themes covered during the first semester of their World History course.
This exam plays a crucial role in students’ academic progress, as it allows them to demonstrate their knowledge and skills acquired throughout the semester. A strong performance on this exam can not only boost their confidence but also provide valuable insights into areas where they may need additional support.
World history semester 1 exam is coming up soon. While studying about the ancient civilizations, I couldn’t help but wonder how much is a bushel of pears ? This question may seem irrelevant, but it actually relates to the topic of trade and commerce in ancient times.
After all, knowing the price of everyday goods can give us insights into the economic conditions of a society. As I continue to prepare for my world history semester 1 exam, I’ll keep this question in mind and see if I can find the answer in my textbooks.
Purpose of the Exam
- Assess students’ understanding of historical concepts, events, and themes
- Evaluate students’ ability to analyze and interpret historical evidence
- Identify areas where students may need additional support
- Provide feedback to students on their academic progress
Significance for Students, World history semester 1 exam
- Contributes to their overall course grade
- Helps them prepare for future assessments, including standardized tests
- Provides an opportunity to reflect on their learning and identify areas for improvement
Historical Periods and Events

The exam covers several major historical periods, each with its own key events and developments.
Understanding the sequence and significance of these periods is crucial for comprehending the evolution of human civilization.
Ancient Civilizations
The ancient world witnessed the rise and fall of several influential civilizations, including:
- Mesopotamia (c. 3500-539 BCE): Cradle of writing, mathematics, and astronomy.
- Ancient Egypt (c. 3100-30 BCE): Known for its monumental architecture, hieroglyphic writing, and advanced medical knowledge.
- Indus Valley Civilization (c. 2600-1900 BCE): Flourished in present-day Pakistan and India, renowned for its urban planning and sophisticated sanitation systems.
- Ancient Greece (c. 800-146 BCE): Birthplace of democracy, philosophy, and the Olympic Games.
- Ancient Rome (c. 753 BCE-476 CE): Vast empire that left a lasting legacy in law, architecture, and infrastructure.
The Middle Ages
The Middle Ages, also known as the Medieval period, spanned from the fall of the Roman Empire to the Renaissance:
- Early Middle Ages (c. 476-1000 CE): Characterized by political fragmentation, the rise of feudalism, and the spread of Christianity.
- High Middle Ages (c. 1000-1300 CE): Period of economic growth, population increase, and cultural advancements, including the Crusades.
- Late Middle Ages (c. 1300-1500 CE): Marked by the Black Death, the Hundred Years’ War, and the decline of feudalism.
Modern History
Modern history encompasses the period from the Renaissance to the present day:
- Renaissance (c. 14th-17th centuries): Rebirth of classical learning, art, and science, leading to the Scientific Revolution.
- Age of Exploration (c. 15th-17th centuries): European powers explored and colonized new territories, transforming global trade and politics.
- Enlightenment (c. 18th century): Period of intellectual and philosophical advancements, emphasizing reason and individualism.
- 20th Century (c. 1900-2000): Characterized by major wars, technological breakthroughs, and social and political changes.
- 21st Century (c. 2000-present): Era of globalization, digital technology, and ongoing social and environmental challenges.
li>Industrial Revolution (c. 18th-19th centuries): Technological advancements that led to mass production and urbanization.
Geographical Regions
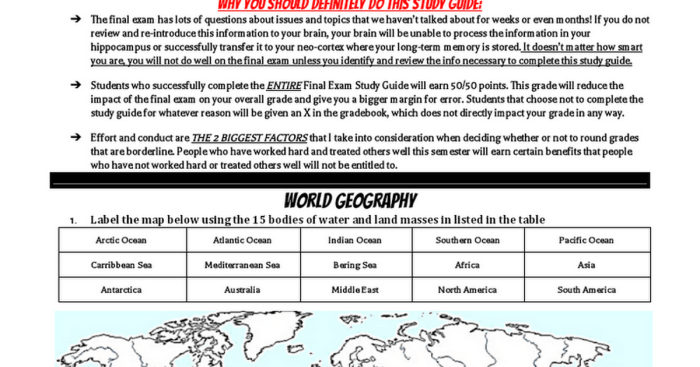
The world history exam encompasses a vast geographical scope, spanning across different continents and regions. Understanding the unique characteristics and contributions of each region is crucial for comprehending global historical developments.
Europe
Europe, a cradle of civilization, has witnessed the rise and fall of numerous empires and civilizations. Important countries to consider include:
- Greece: Known for its philosophy, art, and democracy.
- Rome: Established a vast empire and developed a comprehensive legal system.
- France: A center of Enlightenment and artistic movements.
- Great Britain: Played a significant role in global exploration and industrialization.
Asia
Asia, the largest continent, is home to diverse cultures and ancient civilizations. Key countries and regions include:
- China: Developed advanced civilizations, including the Qin and Han dynasties.
- India: Birthplace of Hinduism, Buddhism, and the Indus Valley Civilization.
- Japan: Known for its unique culture, samurai traditions, and technological advancements.
- Southeast Asia: A crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, with civilizations such as the Khmer Empire.
Africa
Africa, the cradle of humanity, has a rich and diverse history. Important regions and civilizations include:
- Egypt: Developed one of the world’s earliest civilizations along the Nile River.
- West Africa: Home to powerful empires such as Ghana, Mali, and Songhai.
- Southern Africa: Site of the Bantu expansion and the rise of kingdoms like the Zulu.
- East Africa: A hub for trade and cultural exchange, with civilizations such as Aksum.
Americas
The Americas, once home to indigenous civilizations, were later colonized by European powers. Important regions and civilizations include:
- Mesoamerica: Center of advanced civilizations such as the Maya, Aztec, and Inca.
- North America: Inhabited by various Native American tribes before European colonization.
- South America: Home to the Spanish and Portuguese empires and civilizations like the Incas.
- Caribbean: A region of cultural and historical interaction between indigenous peoples, Europeans, and Africans.
Historical Figures

Throughout history, certain individuals have emerged as influential figures, shaping the course of events and leaving lasting legacies. This section highlights key historical figures who played significant roles in the events and developments covered in this semester’s exam.
Each figure’s biography and contributions will be discussed to provide a comprehensive understanding of their impact on history.
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon, known as Alexander the Great, was born in 356 BCE in Pella, Greece. He became king of Macedon at the age of 20 and embarked on a remarkable military campaign that conquered vast territories, stretching from Greece to India.
Alexander’s military genius and innovative tactics revolutionized warfare. He introduced the use of combined arms, siege warfare, and cavalry charges, which proved highly effective against his opponents. His conquests spread Greek culture and ideas throughout the conquered territories, influencing art, literature, and philosophy for centuries to come.
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general, politician, and dictator who lived from 100 to 44 BCE. He played a pivotal role in the decline of the Roman Republic and the establishment of the Roman Empire.
Caesar’s military campaigns expanded the Roman Republic’s territory and brought Gaul (present-day France) under Roman control. He reformed the Roman army and introduced the Julian calendar, which is still used today. As dictator, Caesar implemented social and economic reforms, including land redistribution and citizenship rights for provincials.
Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator was the last pharaoh of ancient Egypt, ruling from 51 to 30 BCE. Known for her intelligence, beauty, and political acumen, she played a significant role in Egyptian history and Roman politics.
Cleopatra formed alliances with Julius Caesar and later Mark Antony, seeking to maintain Egypt’s independence from Roman domination. She patronized the arts and sciences, and her reign saw the construction of iconic monuments such as the Temple of Isis and the Lighthouse of Alexandria.
Exam Format and Structure: World History Semester 1 Exam
The world history semester 1 exam will assess your knowledge and understanding of the material covered throughout the semester. The exam will consist of various question types, including multiple choice, short answer, and essay questions.
To prepare for the exam, it is important to review the course materials, including your notes, textbooks, and any additional resources provided by your instructor. Additionally, consider forming study groups with classmates to discuss the material and test each other’s understanding.
Question Types
- Multiple Choice:These questions will present you with a question or statement followed by several possible answers. Choose the answer that you believe is correct.
- Short Answer:These questions will require you to provide a brief, concise answer to a question or prompt. Your answer should be specific and to the point.
- Essay Questions:These questions will require you to write a more in-depth response to a specific topic or question. Your essay should be well-organized, supported by evidence from the course material, and demonstrate your understanding of the topic.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the purpose of the World History Semester 1 Exam?
To assess your understanding of key historical periods, events, regions, and figures from the dawn of civilization to the modern era.
What types of questions can I expect on the exam?
Multiple choice, short answer, essay, and document-based questions.
How can I prepare for the exam?
Review your notes, study the textbook, and practice answering different types of questions.