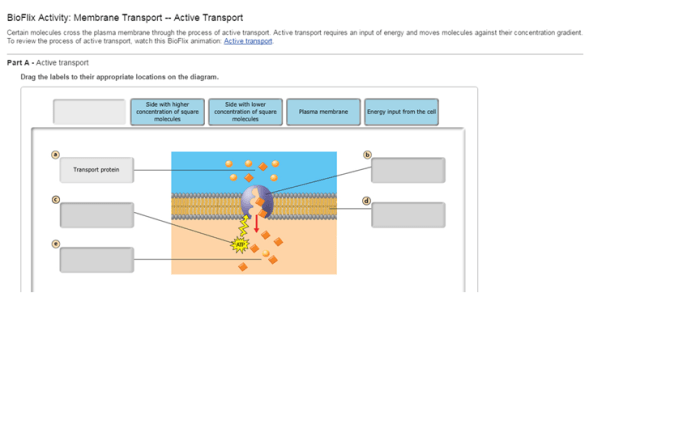
Bioflix activity membrane transport active transport – Embark on a scientific odyssey with Bioflix Activity: Membrane Transport and Active Transport, where we delve into the fascinating world of cellular transport. This immersive learning experience unravels the intricacies of membrane transport, a fundamental process that underpins the very essence of life.
From the passive diffusion of molecules to the energy-driven active transport of ions and nutrients, this analysis provides a comprehensive exploration of the mechanisms and significance of membrane transport. Join us as we uncover the vital role of active transport in maintaining cellular homeostasis, facilitating physiological functions, and driving essential biological processes.
Bioflix Activity Membrane Transport
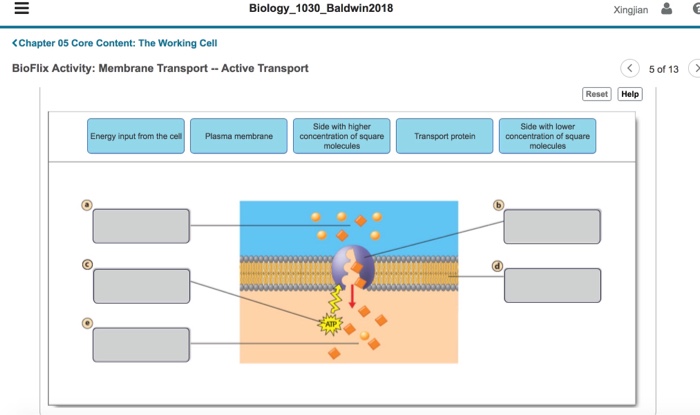
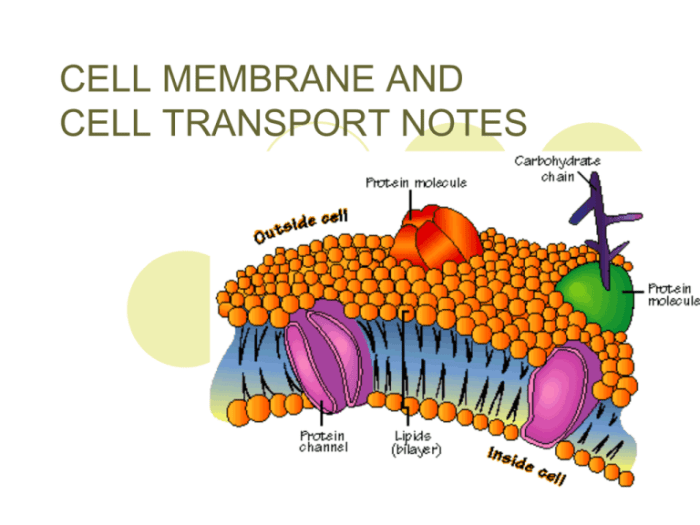
Membrane transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane. It is essential for a variety of biological processes, such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cell signaling. There are two main types of membrane transport: passive transport and active transport.
Passive transport is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This type of transport does not require energy. Active transport is the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
This type of transport requires energy.
Active Transport
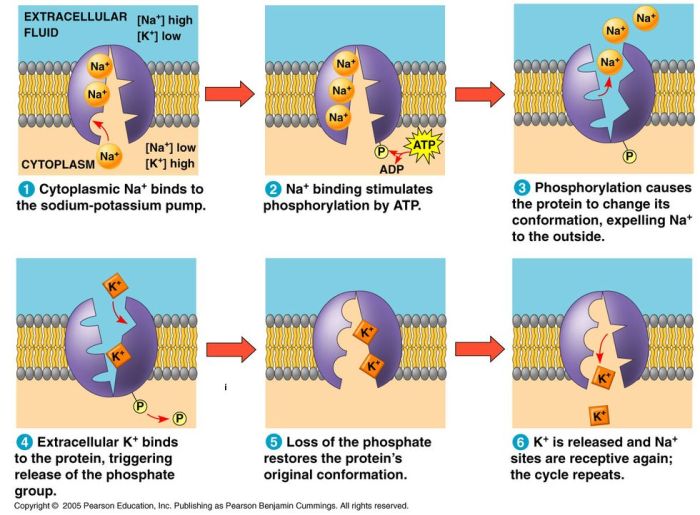
Active transport is a process that uses energy to move molecules across a cell membrane. The energy is used to change the shape of a membrane protein, which then allows the molecule to pass through. Active transport is used to move a variety of molecules, including ions, sugars, and amino acids.
There are two main types of active transport: primary active transport and secondary active transport. Primary active transport uses energy from ATP to move molecules across a cell membrane. Secondary active transport uses the energy stored in a concentration gradient to move molecules across a cell membrane.
Importance of Active Transport, Bioflix activity membrane transport active transport
Active transport is essential for a variety of cellular functions. It is used to maintain cellular homeostasis, which is the balance of the cell’s internal environment. Active transport is also used to transport molecules into and out of cells, which is essential for cell growth and function.
Regulation of Active Transport
Active transport is regulated by a variety of mechanisms. These mechanisms include changes in the concentration of ATP, changes in the concentration of the molecule being transported, and changes in the activity of membrane proteins.
Comparison with Passive Transport
Active and passive transport are two different types of membrane transport. Active transport requires energy, while passive transport does not. Active transport can move molecules against a concentration gradient, while passive transport cannot. Active transport is used to move a variety of molecules, while passive transport is used to move a limited number of molecules.
| Characteristic | Active Transport | Passive Transport |
|---|---|---|
| Energy requirement | Yes | No |
| Direction of movement | Against a concentration gradient | Down a concentration gradient |
| Molecules transported | Variety of molecules | Limited number of molecules |
Applications of Active Transport
Active transport has a variety of applications in medicine and biotechnology. It is used to deliver drugs to cells, to remove toxins from cells, and to separate molecules.
Essential FAQs: Bioflix Activity Membrane Transport Active Transport
What is the primary function of active transport?
Active transport is responsible for moving molecules against their concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration.
How does active transport differ from passive transport?
Active transport requires energy input, typically in the form of ATP, while passive transport does not.
What are some examples of active transport in biological systems?
Examples include the sodium-potassium pump, which maintains ion gradients across cell membranes, and the calcium pump, which transports calcium ions out of cells.
How is active transport regulated?
Active transport is regulated by various mechanisms, including changes in membrane permeability, the availability of energy sources, and the activity of transport proteins.