The nominal ocular hazard distance (NOHD) plays a pivotal role in laser safety, serving as a critical parameter for assessing the potential hazards posed by laser radiation to the human eye. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of the NOHD, exploring its significance, influencing factors, calculation methods, applications, and limitations.
Understanding the NOHD is essential for ensuring the safe use of lasers in various fields, including laser safety, laser marking, and laser surgery. This guide provides a thorough overview of the NOHD, empowering readers with the knowledge and tools to effectively mitigate ocular hazards associated with laser radiation.
Define the Nominal Ocular Hazard Distance (NOHD)
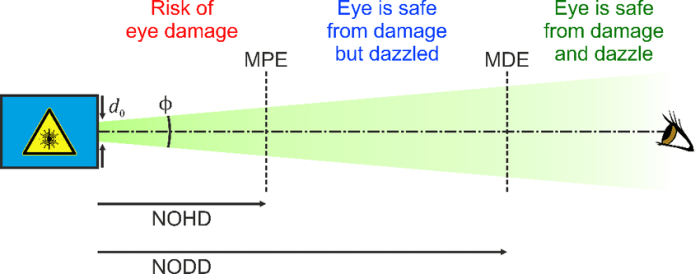
The Nominal Ocular Hazard Distance (NOHD) is a critical parameter used to assess the potential ocular hazards associated with laser radiation. It is defined as the minimum distance at which an individual’s eye is considered to be safe from damage caused by the laser beam.
The NOHD is determined by various factors, including the laser’s wavelength, power, beam divergence, and exposure duration. It is crucial for laser safety to establish the NOHD and ensure that personnel working with lasers maintain a safe distance to minimize the risk of ocular injury.
Factors Influencing the NOHD: The Nominal Ocular Hazard Distance
- Laser wavelength:Different wavelengths of laser light have varying degrees of absorption by the eye’s tissues. Shorter wavelengths, such as ultraviolet (UV) and blue light, are more hazardous to the eye than longer wavelengths, such as infrared (IR) light.
- Laser power:The higher the laser power, the greater the potential for ocular damage. High-power lasers can cause burns and other injuries to the retina and other eye structures.
- Beam divergence:The divergence of the laser beam affects the size of the beam spot on the eye. A more divergent beam will result in a larger spot size, reducing the power density and potentially decreasing the risk of ocular injury.
- Exposure duration:The duration of exposure to laser radiation is also a critical factor. Longer exposure times increase the risk of ocular damage, even at lower power levels.
Calculating the NOHD
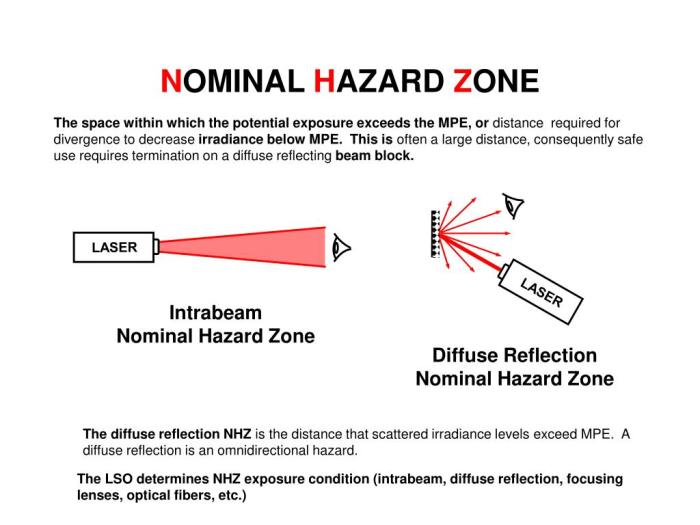
The NOHD can be calculated using various methods, depending on the type of laser and the available information.
For continuous wave (CW) lasers, the NOHD can be calculated using the following formula:
NOHD = (MPL / (E × t))1/2
where:
- MPL is the Maximum Permissible Exposure for the given laser wavelength and exposure duration
- E is the irradiance at the cornea (in W/cm 2)
- t is the exposure duration (in seconds)
For pulsed lasers, the NOHD calculation is more complex and requires additional parameters, such as pulse duration and repetition rate.
Applications of the NOHD
The NOHD is widely used in various fields to ensure laser safety:
- Laser safety programs:The NOHD is a fundamental parameter for establishing laser safety protocols and determining safe working distances for personnel.
- Laser marking:In laser marking applications, the NOHD helps ensure that operators are at a safe distance from the laser beam during the marking process.
- Laser surgery:In medical settings, the NOHD is used to determine safe distances for surgeons and other personnel during laser surgery procedures.
Limitations of the NOHD

While the NOHD is a valuable tool for assessing ocular hazards, it has certain limitations:
- Applicability:The NOHD is only applicable for assessing ocular hazards from direct laser radiation. It does not consider indirect hazards, such as reflections or scattered light.
- Accuracy:The NOHD calculation relies on accurate measurements of laser parameters, such as power and beam divergence. Inaccuracies in these measurements can affect the accuracy of the NOHD.
Related Concepts
The NOHD is closely related to other laser safety concepts:
- Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE):The MPE is the maximum amount of laser radiation that can be safely incident on the eye or skin without causing damage. The NOHD is derived from the MPE.
- Laser classification standards:Laser classification standards, such as those defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), use the NOHD to classify lasers into different hazard classes.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of the NOHD?
The NOHD is used to determine the minimum safe distance from a laser source at which the eye is protected from potential hazards.
What factors influence the NOHD?
Factors that influence the NOHD include laser wavelength, power, beam divergence, and exposure duration.
How is the NOHD calculated?
The NOHD can be calculated using various methods, depending on the type of laser and the available information.