The endocrine system worksheet answer key unveils the intricacies of the endocrine system, a complex network of glands responsible for hormone production and regulation. This key provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the function, mechanisms, and clinical applications of the endocrine system, empowering learners to delve into the fascinating world of hormone signaling and its impact on human health.
Delving into the depths of the endocrine system, this worksheet answer key unravels the mechanisms by which hormones are synthesized, released, and interact with target cells. It explores the intricate dance of negative feedback loops and the role of the nervous system in maintaining hormonal balance, providing a thorough understanding of the body’s delicate hormonal orchestra.
1. Define the Endocrine System

The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate a wide range of bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood.
The endocrine system is essential for maintaining homeostasis, the body’s internal balance. Hormones work in conjunction with the nervous system to control and coordinate the body’s response to internal and external stimuli.
Types of Endocrine Glands
There are two main types of endocrine glands:
- Endocrine glandssecrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
- Exocrine glandssecrete hormones into ducts that lead to the body’s surface or to the digestive tract.
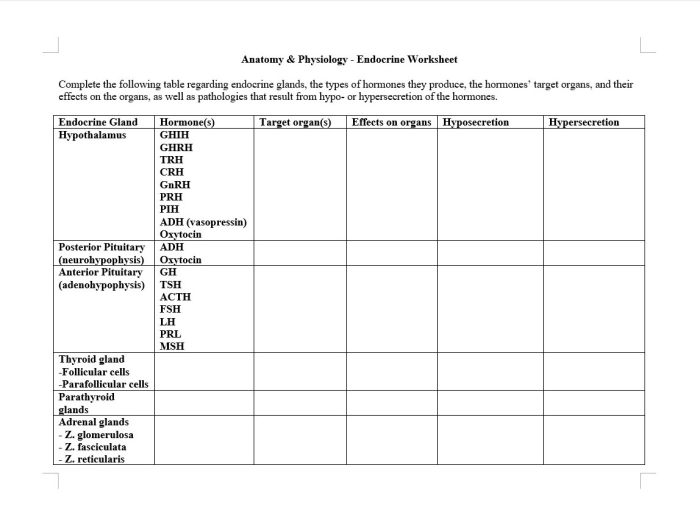
The major endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes.
2. Hormones and their Mechanisms of Action
Definition and Chemical Structure of Hormones
Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced and secreted by endocrine glands. They are typically proteins, peptides, or steroids.
Synthesis, Storage, and Release of Hormones
Hormones are synthesized in the endocrine glands and stored in vesicles until they are released into the bloodstream in response to specific stimuli.
Mechanisms of Hormone Action, Endocrine system worksheet answer key
Hormones can exert their effects on target cells through various mechanisms:
- Binding to cell surface receptors: Hormones bind to specific receptors on the surface of target cells, triggering a cascade of intracellular events that lead to a cellular response.
- Binding to intracellular receptors: Some hormones can cross the cell membrane and bind to receptors inside the cell, directly regulating gene expression.
Types of Hormone Receptors
There are two main types of hormone receptors:
- G protein-coupled receptors: These receptors are located on the cell surface and are coupled to G proteins, which activate intracellular signaling pathways.
- Nuclear receptors: These receptors are located inside the cell and bind to hormones that can cross the cell membrane. They regulate gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences.
3. Regulation of Hormone Secretion
The secretion of hormones is tightly regulated to maintain hormone balance and ensure appropriate physiological responses.
Mechanisms of Regulation
The secretion of hormones is regulated by various mechanisms, including:
- Negative feedback loops: Hormones often inhibit their own secretion through negative feedback loops. When hormone levels rise, they signal the endocrine gland to decrease hormone production.
- Positive feedback loops: In some cases, hormones can stimulate their own secretion through positive feedback loops. This is less common than negative feedback.
- Circadian rhythms: The secretion of some hormones, such as cortisol, follows a circadian rhythm, with levels varying throughout the day.
Role of the Nervous System
The nervous system also plays a role in regulating hormone secretion. For example, the hypothalamus controls the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland.
4. Disorders of the Endocrine System
Disorders of the endocrine system can occur due to various factors, including genetic defects, autoimmune diseases, and tumors.
Types of Endocrine Disorders
Some common endocrine disorders include:
- Diabetes: A disorder in which the body cannot properly regulate blood sugar levels.
- Thyroid disorders: Disorders that affect the function of the thyroid gland, leading to either hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid).
- Growth hormone disorders: Disorders that affect the secretion of growth hormone, leading to either gigantism (excessive growth) or dwarfism (short stature).
5. Clinical Applications of Endocrinology: Endocrine System Worksheet Answer Key
Endocrinologists are medical professionals who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of endocrine disorders.
Diagnostic Tests
Endocrinologists use various diagnostic tests to evaluate hormone levels and assess the function of the endocrine system, including:
- Blood tests: Blood tests can measure hormone levels and assess the function of specific endocrine glands.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as ultrasound and MRI scans, can visualize the endocrine glands and assess their structure and function.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for endocrine disorders vary depending on the specific disorder and its severity, and may include:
- Hormone replacement therapy: In cases of hormone deficiency, hormone replacement therapy can be used to restore hormone levels.
- Medication: Medications can be used to inhibit or stimulate hormone production or block the effects of hormones.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove tumors or other abnormalities of the endocrine glands.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the function of the endocrine system?
The endocrine system regulates various bodily functions through the production and secretion of hormones, chemical messengers that travel through the bloodstream to target cells.
How are hormones regulated?
Hormone secretion is regulated by negative feedback loops, where the level of a hormone in the bloodstream influences its own production and release.
What are some common endocrine disorders?
Common endocrine disorders include diabetes, thyroid disorders, and growth hormone disorders, each with its unique symptoms and treatment approaches.