Federalism activity classifying government powers, a topic of paramount importance, invites us to delve into a discourse that illuminates the intricate mechanisms of governance. This comprehensive exploration will unravel the complexities of federal systems, examining the division of powers between federal and state governments, the impact of the Supremacy Clause, the dynamics of concurrent powers, and the multifaceted nature of intergovernmental relations.
Prepare to embark on an intellectual journey that empowers you with a profound understanding of this fundamental aspect of political science.
In this discourse, we will dissect the concept of federalism, exploring its advantages and disadvantages, and examining real-world examples of federal systems. We will delve into the intricacies of power division, analyzing the criteria for assigning powers to different levels of government.
The Supremacy Clause will be examined, highlighting its impact on the relationship between federal and state laws. Concurrent powers, shared by both federal and state governments, will be explored, along with the challenges and opportunities they present.
Introduction
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central government and several regional governments. This division of power can be based on geography, ethnicity, or other factors. Federal systems are often created in order to protect the rights of minority groups or to promote economic development in different regions of a country.
Some examples of federal systems include the United States, Canada, Australia, and Germany. In the United States, the federal government is responsible for matters such as foreign policy, defense, and interstate commerce. The state governments are responsible for matters such as education, healthcare, and law enforcement.
There are several advantages to federalism. First, it can help to protect the rights of minority groups. This is because the federal government can intervene to protect the rights of minorities if the state governments fail to do so. Second, federalism can promote economic development in different regions of a country.
This is because the federal government can provide financial assistance to states that are struggling economically.
However, there are also some disadvantages to federalism. First, it can lead to conflict between the federal and state governments. This is because the federal government and the state governments may have different priorities. Second, federalism can be inefficient. This is because the federal government and the state governments may duplicate services.
Division of Powers: Federalism Activity Classifying Government Powers
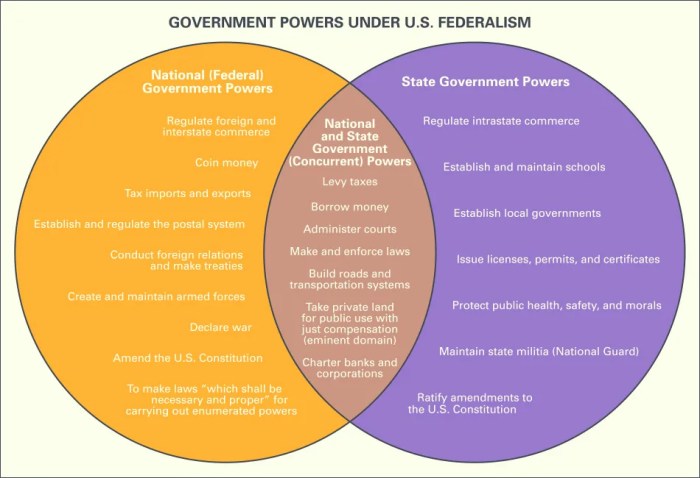
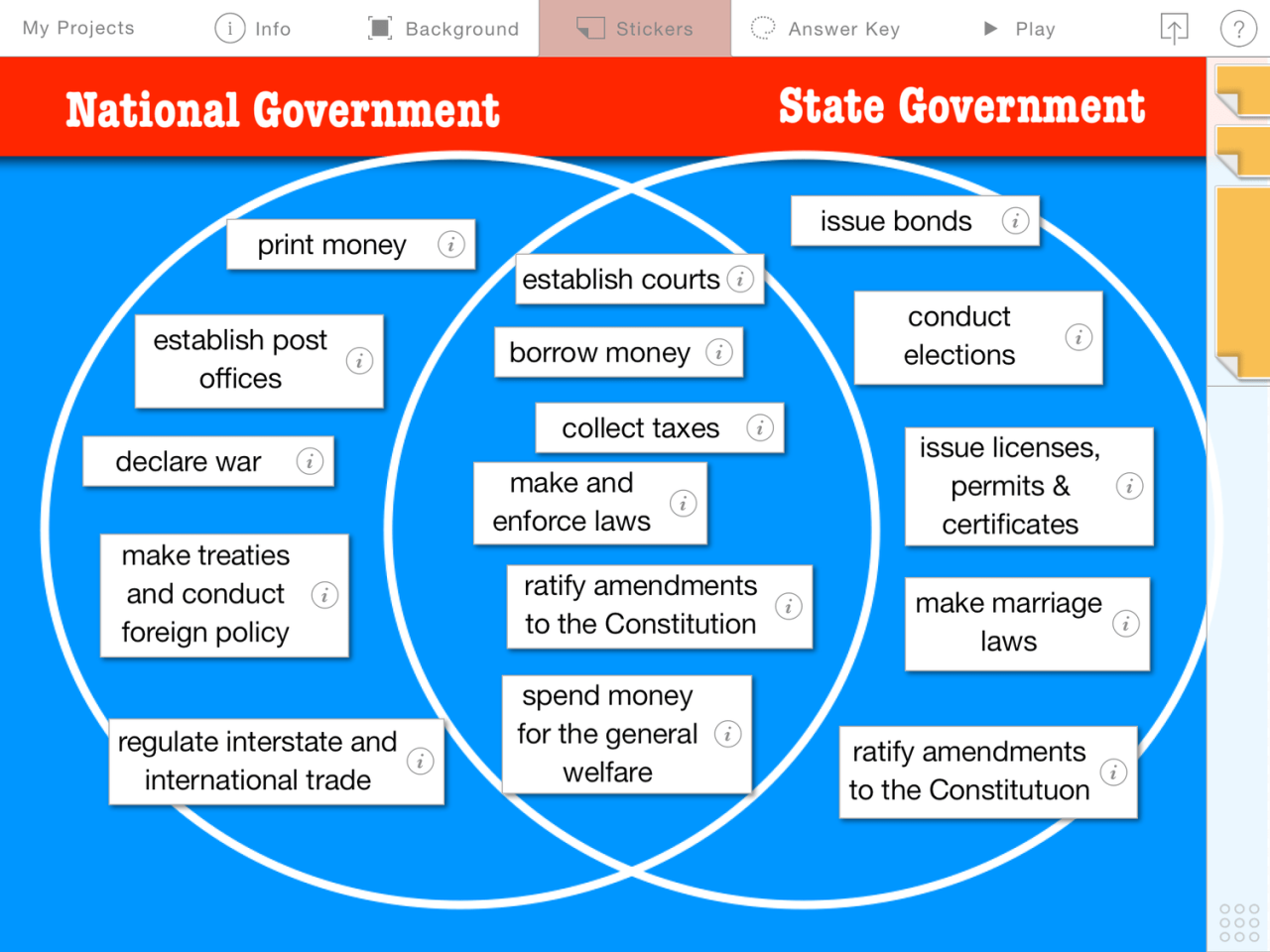
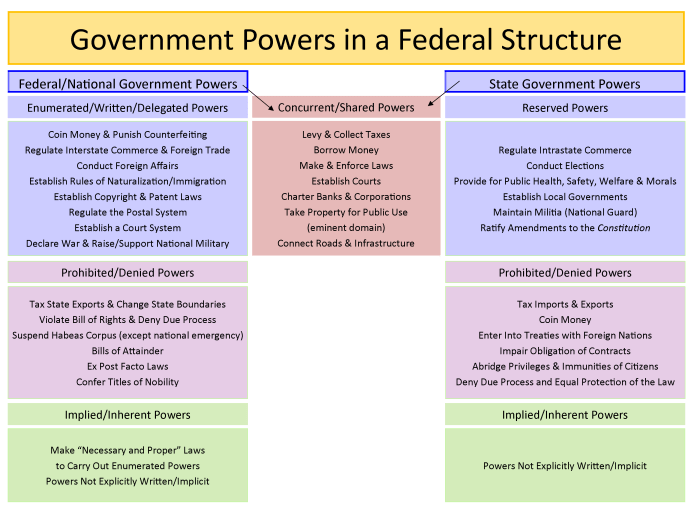
In a federal system, the powers of the federal and state governments are typically divided into three categories: exclusive powers, concurrent powers, and reserved powers.
- Exclusive powersare powers that are granted only to the federal government. These powers include the power to declare war, to make treaties, and to regulate interstate commerce.
- Concurrent powersare powers that are shared by the federal government and the state governments. These powers include the power to tax, to borrow money, and to establish courts.
- Reserved powersare powers that are not granted to the federal government or to the state governments. These powers are reserved to the people.
The division of powers between the federal and state governments is not always clear-cut. There are often disputes over which government has the authority to regulate a particular issue. These disputes are typically resolved by the courts.
Exclusive Powers of the Federal Government
- Declare war
- Make treaties
- Regulate interstate commerce
- Coin money
- Establish a postal system
- Maintain an army and navy
- Establish courts
Concurrent Powers of the Federal and State Governments, Federalism activity classifying government powers
- Tax
- Borrow money
- Establish courts
- Regulate commerce within their borders
- Provide for the health and welfare of their citizens
Reserved Powers of the People
- The right to vote
- The right to free speech
- The right to bear arms
- The right to assemble
- The right to petition the government
FAQ Insights
What is the primary advantage of federalism?
Federalism allows for both centralized authority and local autonomy, providing a balance between national unity and regional diversity.
How does the Supremacy Clause impact the relationship between federal and state laws?
The Supremacy Clause establishes the supremacy of federal law over state law, ensuring uniformity and consistency in matters of national importance.
What are the challenges associated with concurrent powers?
Concurrent powers can lead to conflicts and inefficiencies when federal and state governments exercise overlapping authority in the same policy areas.