That the tharsis region on mars has so few craters – The Tharsis region on Mars is a vast volcanic province that covers a quarter of the planet’s surface. Despite its size, the region has surprisingly few craters, raising questions about its geological history and the processes that have shaped it.
This article explores the reasons why the Tharsis region has so few craters, examining the factors that influence crater formation and preservation on Mars.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
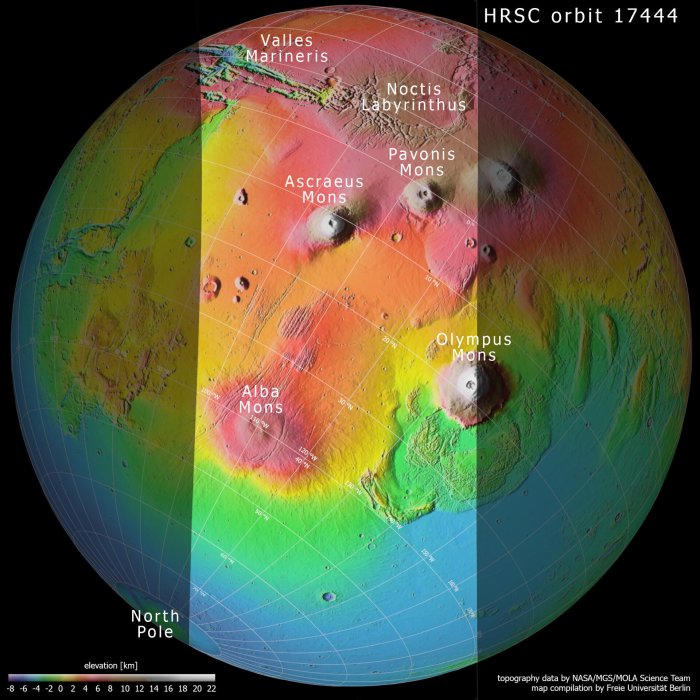
Overview of the Tharsis Region on Mars

The Tharsis region on Mars is a vast volcanic province located in the western hemisphere of the planet. It covers an area of approximately 10,000 kilometers across and is characterized by a complex array of volcanoes, calderas, and lava flows.
The region is home to some of the largest volcanoes in the Solar System, including Olympus Mons, which is over 21 kilometers high and is the tallest mountain in the Solar System. The Tharsis region is also the location of the Valles Marineris, a system of canyons that stretch for over 4,000 kilometers and are up to 7 kilometers deep.
The Tharsis region is a major feature of Martian geology and has played a significant role in shaping the planet’s surface and atmosphere.
Crater Distribution on Mars
The distribution of craters on Mars provides important insights into the planet’s geological history. Craters are formed by the impact of meteoroids and asteroids on the surface of a planet, and their density can be used to estimate the age of the surface.
The Tharsis region has a relatively low crater density compared to other regions on Mars, indicating that the surface of the region is relatively young. This is likely due to the volcanic activity in the region, which has resurfaced the area and erased older craters.
Factors Influencing Crater Formation: That The Tharsis Region On Mars Has So Few Craters
The formation and preservation of craters on Mars are influenced by a number of factors, including surface age, erosion, and volcanic activity. The surface age of a region is a major factor in determining the number of craters it has.
Older surfaces have more time to accumulate craters, while younger surfaces have fewer craters. Erosion can also remove craters from the surface of a planet, especially if the erosion is caused by wind or water. Volcanic activity can also resurface a planet’s surface, erasing older craters and creating new ones.
Geological Processes in the Tharsis Region
The Tharsis region has been shaped by a number of geological processes, including volcanic activity, tectonic deformation, and erosion. Volcanic activity has played a major role in the formation of the Tharsis region, creating the volcanoes, calderas, and lava flows that characterize the region.
Tectonic deformation has also played a role in shaping the Tharsis region, creating the Valles Marineris and other canyons in the region. Erosion has also played a role in shaping the Tharsis region, removing older craters and creating new ones.
FAQ Guide
Why does the Tharsis region have so few craters?
The low crater density in the Tharsis region is attributed to ongoing volcanic activity, which has resurfaced the area and erased craters over time.
What factors influence crater formation on Mars?
Crater formation on Mars is influenced by surface age, erosion, and volcanic activity. Older surfaces have more craters, while erosion and volcanic eruptions can remove or modify craters.
What are the implications of the low crater density in the Tharsis region?
The low crater density suggests that the Tharsis region has been volcanically active for a prolonged period, providing insights into the geological history and evolution of Mars.